Share
Autism and ABA Overview
Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is a neurological and development disorder that impacts social interactions, communication, learning, and behavior. ASD prevalence is estimated at ~2.3% across children aged 3-17 and has increased over the last decade primarily due to the inclusion of other disorders into ASD (e.g. Asperger’s Syndrome) and increased screening. The symptoms associated with ASD generally appear in the first two years of life.
Applied behavioral analysis (ABA) is a specialized therapy and is considered to be the most effective treatment for autism, a claim supported by a number of peer-reviewed publications and empirical research. Coverage for ABA therapy is almost ubiquitously mandated in the U.S. across payer types.
The core approach of ABA is predicated on reinforcing helpful behaviors while not reinforcing unhelpful or harmful behaviors, leading to permanent change. ABA treatment takes place in a variety of settings including in-home therapy, community or center-based treatment, and treatment in schools. Therapy intensity varies and is usually correlated with age. Younger children not yet of school age typically receive the most amount of care, which can often be in excess of 40+ hours per week.
ABA Industry Overview
ABA treatment is led by a Board-Certified Behavior Analyst (BCBA), a graduate-level clinician certified in behavioral analysis. BCBAs write and oversee care plans for ASD treatment, while Registered Behavior Technicians (RBTs) typically spend the most time with patients and are responsible for the implementation of ABA therapy.
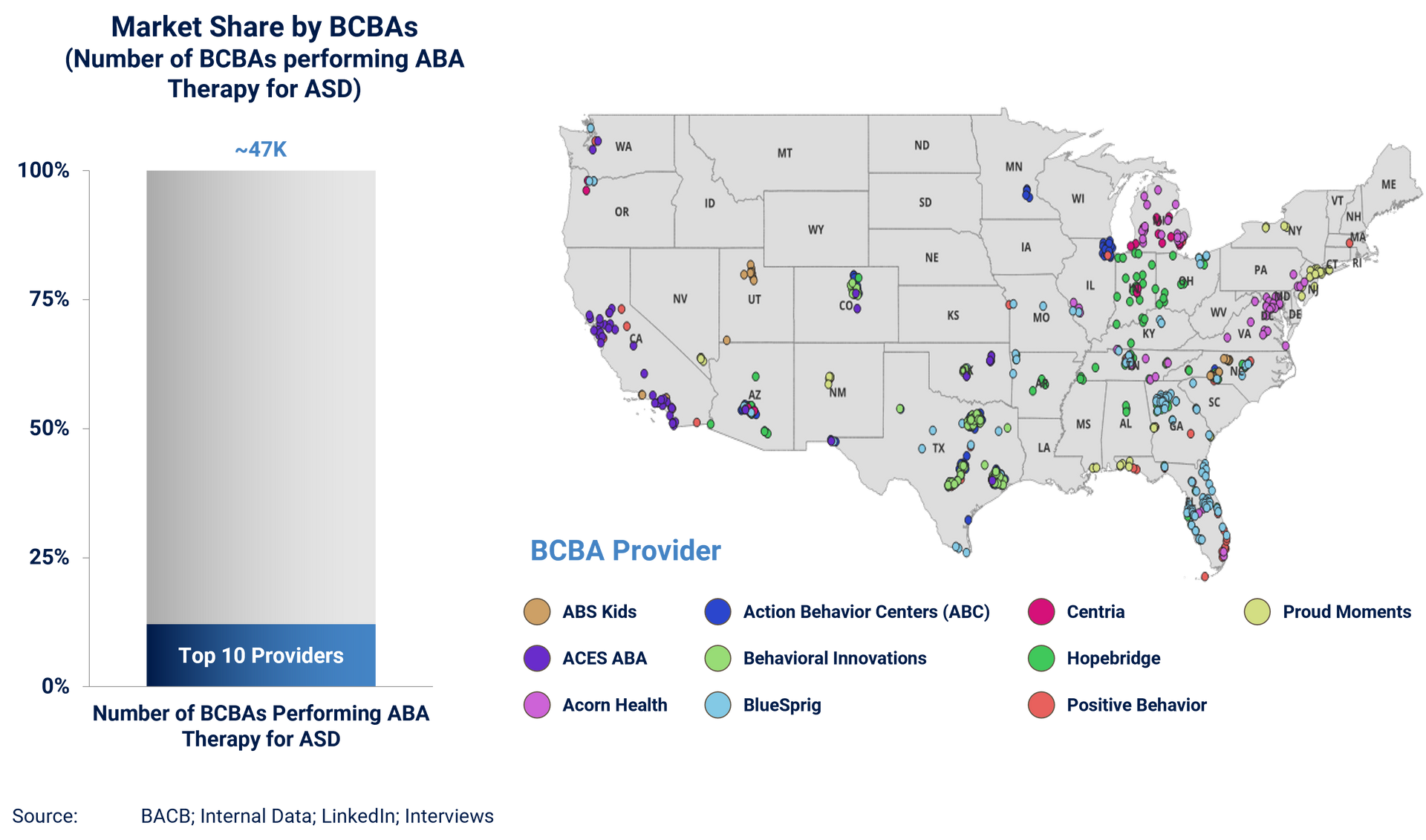
ABA Therapy Market Size
Currently, there is a significant supply and demand imbalance between the number of ABA providers and the number of children that require care. Based on current prevalence rates across children aged 3-17, there are ~600k children in the United States that require care, translating to a total addressable market opportunity of ~$30b-$40b. However, there are currently only ~68k BCBAs in the U.S., of which ~47k actively treat ASD patients, implying a realized market size of only ~$13B-$21B.
ABA Trends & Drivers
Due to the significant supply-demand gap, growth historically has only been throttled by the amount of BCBAs, which has grown at a healthy ~13% annually over the last five years (2019-2024)—signifying a continued growth trajectory.
Growth potential in the ABA space also can be attributed to underlying demand. In 2000, 1 in 150 were estimated to have ASD, but now the number has more than doubled to 1 in 44 as of 2022.
Further, the ABA space has benefited from several regulatory and policy changes. In 2008, the Mental Health Parity and Addiction Equity Act was enacted, requiring health insurers to provide the same level of benefits for mental and/or substance use treatment and services.
The Autism CARES Act of 2019 provided an additional $369.7 million towards autism efforts in annual federal spending. This act also expanded the focus of some government activities to account for the lifespan of those on the autism spectrum requiring the proper reports are sent to Congress.
Provider Landscape
The ABA provider landscape is highly fragmented as the top 10 players in the U.S. account for only ~10-15% of market share, with most of these providers being regionally focused. Consolidated players tend to be center-based and include BlueSprig in the South and Mid-West, Action Behavioral Centers (ABC) focused on Texas and surrounding market, and ACES ABA on the West Coast.
Investment Considerations
The ABA market remains primed for near-term growth and further consolidation. At Stax, we typically focus on a number of considerations when advising on an investment in ABA and similar assets:
- Competitive Density – The ABA market, much like the rest of healthcare, is highly localized. Understanding the competitive market density of other providers and the ownership structure (e.g., independents vs. scaled PE-backed players) is critical to evaluating the likelihood of success.
- Payer Dynamics – Prevailing market rates across payer types is also essential to understand. The favorability of rates is often impacted by concentration (and leverage) of payers in a given market. Local supply and demand conditions can also impact provider leverage.
- BCBA and RBT supply levels – Local supply levels and estimated growth rates attached to these levels inform how quickly a practice or platform can scale. Factors typically considered are prevailing wage rates similar to other occupations and the presence of local universities and colleges that funnel new supply into a given market.
- Referral Dynamics – Developmental pediatricians, psychologists, psychiatrists, and other upstream providers can heavily influence patient and family choice of ABA providers. Understanding the density of providers that can diagnose ASD (and therefore create demand for ABA) and their perceptions of the ABA providers in their local markets is highly important to success and sustainability.
To learn more about Stax and our services, including our specialization in the Healthcare industry, visit www.stax.com or click here to contact us directly.







